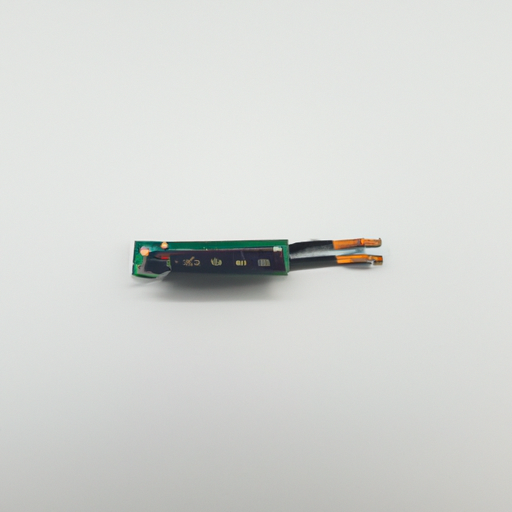
What Components and Modules Does the Connector Contain? IntroductionIn the realm of technology and engineering, connectors play a pivotal role in facilitating communication and power transfer between various components. A connector is defined as a device that joins two or more electrical circuits together, allowing for the transmission of signals or power. Connectors are ubiquitous in numerous applications, including electronics, automotive systems, telecommunications, and industrial machinery. Understanding the components and modules that make up connectors is essential for engineers, designers, and technicians alike, as it can significantly impact the performance and reliability of the systems they work with. This article aims to explore the various components and modules of connectors, shedding light on their functions and importance in modern technology. 1. Understanding Connectors 1.1 Definition and FunctionalityConnectors are devices that establish electrical or mechanical connections between different parts of a system. They serve as the interface that allows for the transfer of power, data, or signals, ensuring that various components can communicate effectively. The functionality of connectors is critical in ensuring that systems operate smoothly and efficiently, making them an integral part of any electronic or mechanical assembly. 1.2 Types of ConnectorsConnectors come in various types, each designed for specific applications. The most common types include electrical connectors, which facilitate the flow of electricity; optical connectors, which transmit light signals; and mechanical connectors, which provide physical connections between components. Selecting the right type of connector is crucial, as it can affect the overall performance, reliability, and safety of the system. 2. Key Components of Connectors 2.1 HousingThe housing of a connector serves as its outer shell, protecting the internal components from environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and mechanical stress. The materials used for housing can vary, with common options including plastic and metal. Design considerations for housing include size, shape, and environmental resistance, ensuring that the connector can withstand the conditions it will be exposed to during its operational life. 2.2 ContactsContacts are the conductive elements within a connector that establish the electrical connection. They can come in various forms, including male and female contacts, pins, and sockets. The materials used for contacts are critical for ensuring good conductivity and resistance to corrosion; common materials include gold and nickel. Additionally, contact configurations can vary, with options for single or multi-pin arrangements, depending on the application requirements. 2.3 InsulationInsulation is a vital component of connectors, as it prevents short circuits and ensures safety during operation. The materials used for insulation can include rubber and thermoplastics, which provide effective barriers against electrical leakage. Key factors to consider in insulation design include dielectric strength and thermal stability, ensuring that the connector can operate safely under various conditions. 2.4 Strain ReliefStrain relief is an essential feature of connectors that helps maintain connection integrity by absorbing mechanical stress. It prevents damage to the internal components caused by bending or pulling on the cable. Strain relief can come in various designs, such as molded or crimped, and plays a significant role in extending the longevity and performance of the connector. 3. Modules in Connectors 3.1 Modular ConnectorsModular connectors are designed to be easily assembled and disassembled, allowing for flexibility in design and application. Examples of modular connectors include RJ45 and RJ11, commonly used in networking and telecommunications. The benefits of modularity include ease of maintenance, customization, and the ability to adapt to changing technological needs. 3.2 Integrated ModulesIntegrated modules within connectors enhance their functionality by combining multiple features into a single unit. Examples include USB and HDMI connectors, which support data transfer, power delivery, and video output. These integrated modules simplify connections and reduce the number of individual components required, streamlining design and improving user experience. 3.3 Custom ModulesCustom modules are essential for specialized applications that require unique connector solutions. The design process for custom modules involves close collaboration between engineers and clients to ensure that the final product meets specific requirements. Industries such as aerospace, medical, and automotive often utilize custom connector modules to address their unique challenges and enhance performance. 4. Advanced Features in Connectors 4.1 Smart ConnectorsSmart connectors represent a new frontier in connector technology, incorporating advanced features such as sensors and data transmission capabilities. These connectors can monitor performance, detect faults, and communicate with other devices, making them ideal for applications in the Internet of Things (IoT) and automation. The integration of smart technology into connectors enhances their functionality and opens up new possibilities for system design. 4.2 Environmental ConsiderationsConnectors designed for harsh environments must meet specific environmental ratings, such as IP ratings, which indicate their resistance to dust and water ingress. Industries such as military and aerospace require connectors that can withstand extreme conditions, including temperature fluctuations, vibration, and exposure to chemicals. The materials and design features of these connectors are tailored to enhance their environmental resistance, ensuring reliable performance in challenging situations. 5. Future Trends in Connector Technology 5.1 MiniaturizationThe trend towards miniaturization in connector design is driven by the demand for smaller, more compact devices. As technology advances, the need for connectors that occupy less space while maintaining functionality becomes increasingly important. Miniaturization impacts design and functionality, allowing for more efficient use of space in applications ranging from consumer electronics to medical devices. 5.2 Wireless ConnectorsThe shift towards wireless connectivity is transforming the landscape of connector technology. Wireless connectors eliminate the need for physical connections, enabling seamless communication between devices. Understanding how wireless connectors function and their implications for traditional connector designs is crucial as industries move towards more flexible and efficient solutions. 5.3 Sustainability in Connector DesignSustainability is becoming a key consideration in connector manufacturing, with an emphasis on using sustainable materials and practices. Companies are increasingly focusing on recycling and end-of-life considerations for connectors, aiming to reduce their environmental impact. Leading companies in the industry are pioneering sustainable connector designs, setting a precedent for future developments. ConclusionIn summary, connectors are essential components in various technological applications, and understanding their design and functionality is crucial for engineers and designers. The key components of connectors, including housing, contacts, insulation, and strain relief, play significant roles in ensuring reliable performance. Additionally, the integration of modular and custom modules enhances the versatility of connectors, while advanced features such as smart technology and environmental considerations pave the way for future innovations. As the industry continues to evolve, trends such as miniaturization, wireless connectivity, and sustainability will shape the future of connector technology, impacting a wide range of industries. References- [Connector Basics](https://www.connector.com)- [Understanding Electrical Connectors](https://www.electricalengineering.com)- [The Future of Connectors: Trends and Innovations](https://www.technologyreview.com)- [Sustainable Practices in Connector Manufacturing](https://www.sustainabilityjournal.com) This blog post provides a comprehensive overview of the components and modules that make up connectors, highlighting their importance in modern technology and the trends shaping their future.